The study of nuclear reactions aims at describing the mechanisms sustaining the evolution of nuclear matter when it undergoes a modification of its state. This modification can occur after an external excitation (e.g., neutron capture) or internal excitation (e.g., beta decay).
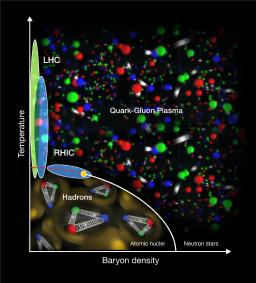
The interaction between quarks and gluons is described by the Quantum Chromo-Dynamics (QCD) theory. This strong interaction confines the quarks and gluons inside the protons, neutrons and other hadrons.
The physics of neutrinos is studied using different sources such as reactors, accelerators and radioactive sources. The objectives of these experiments are: - to measure all neutrino oscillation parameters by varying their energies and oscillation distance and measure their mass.
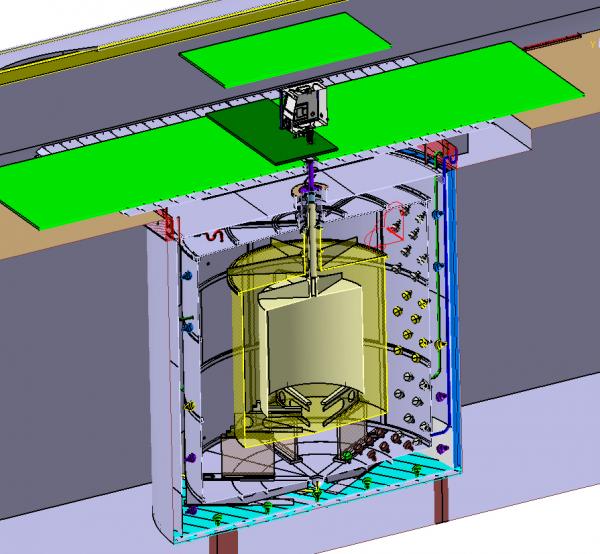
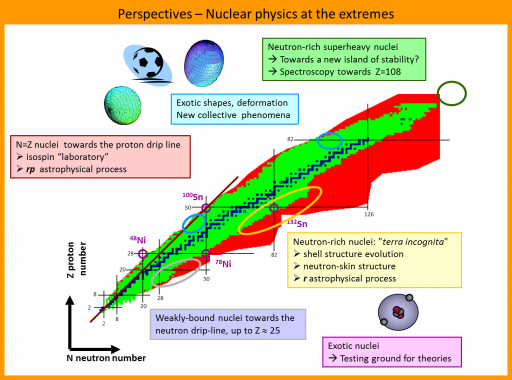
The structural aspect of the atomic nucleus is governed by the interaction between nucleons, protons and neutrons, binded by the strong interaction. This multibody quantum system is often described by a nuclear medium field built on an effective nucleon-nucleon interaction.
Quarks and gluons hadron structure
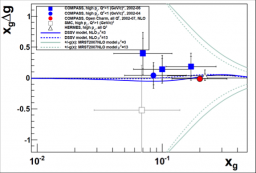
DPhN is strongly engaged in the study of the partonic structure (in terms of quarks and gluons) of nucleons, protons and neutrons. Nucleons are singular objects as about 90% of their mass originates not from their constituent masses, but rather from the strong interaction they experience.