Reaction studies with Relativistic Radioactive Beams
Goals of the experiment
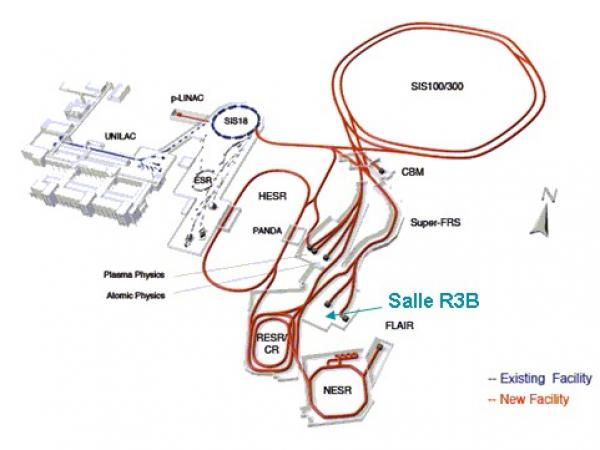
The R3B experiment is part of the FAIR project (Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research, http://www.gsi.de/fair) to be built at GSI (Darmstadt, Germany). The FAIR project gathers different physics around a common facility: exotic nuclei at low and high energy, hadronic physics with proton – antiproton collisions, relativistic heavy-ion collisions (a few 10 GeV per nucleon), plasma physics and atomic physics.
COCOTIER