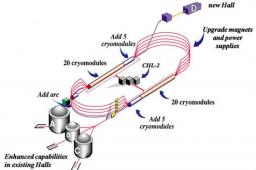
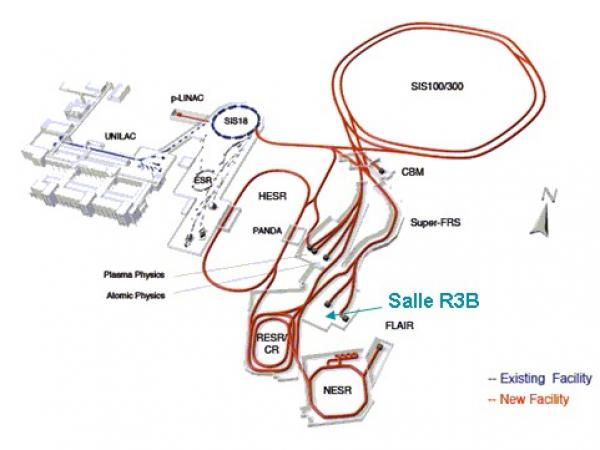
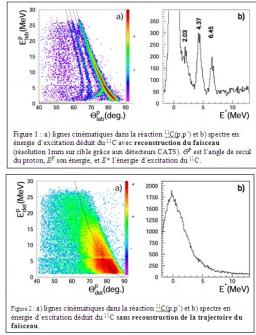
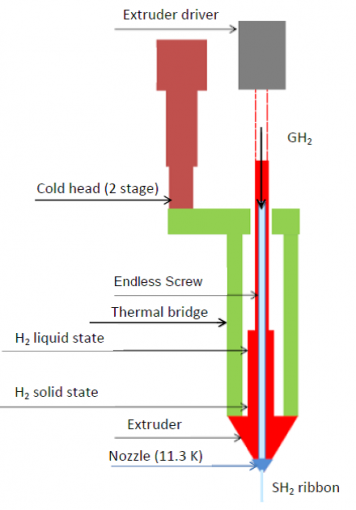
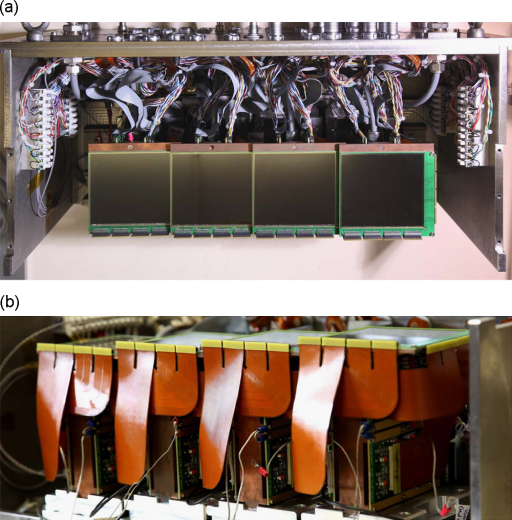
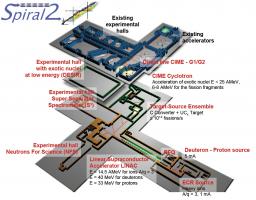
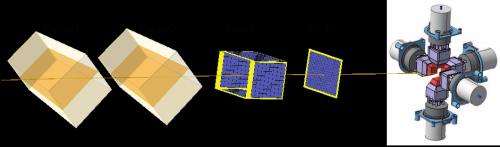
Deeply Virtual Compton Scattering experiment at Jefferson Lab Hall B , with CLAS12, large acceptance spectrometer.
Goals:
Theoretical concepts as Generalized Parton Distributions (GPD), enable to probe with a dramatic accuracy the nucleon structure, and access the quark confinement in hadrons.
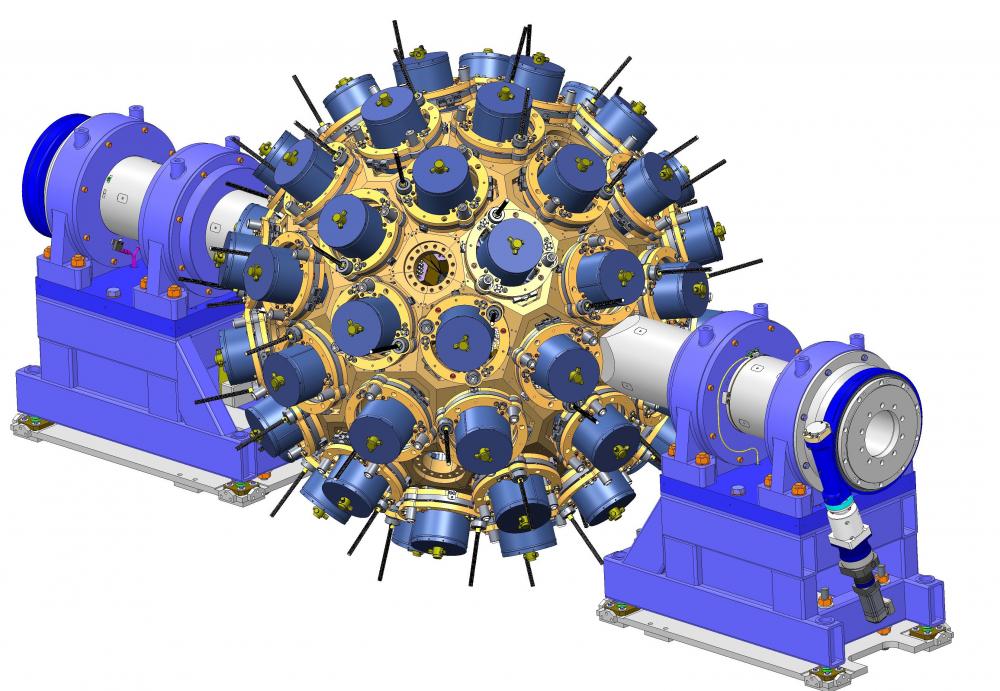
CLAS12-Tracker