Using the European X-ray astronomy satellite XMM-Newton [1], researchers from CNRS [2] and CEA [3] have discovered a new source of cosmic rays. In the vicinity of the remarkable Arches cluster, near the center of the Milky Way, these particles are accelerated in the shock wave generated by tens of thousands of young stars moving at a speed of around 700,000
km/h. These cosmic rays produce a characteristic X-ray emission by interacting with the atoms in the surrounding gas. Their origin differs from that of the cosmic rays discovered exactly a hundred years ago by Victor Hess, which originate in the explosions of supernovae. The findings are published in the October issue of the Astronomy & Astrophysics journal.
Shock from a star cluster
A hundred years ago, the Austrian physicist Victor Franz Hess discovered the existence of ionizing radiation of extraterrestrial origin, which he called cosmic rays. Today, their nature is well understood. When certain stars at the end of their lives explode and become supernovae, their matter is ejected at supersonic speed, generating shock waves that accelerate the particles. As a result, some atomic nuclei gain very high kinetic energy and enter the Earth's atmosphere.
However, low-energy cosmic rays [4] are not detected in the region of our planet, since the solar wind prevents them from entering the heliosphere. Little is therefore known about their chemical composition and flux outside the Solar System, although everything suggests they play a significant role in the Galaxy. For instance, by ionizing and heating the densest interstellar clouds, they probably regulate the formation of stars.
The authors of the article began by studying the X-ray emission that should theoretically be generated by low-energy cosmic rays in the interstellar medium. They then looked for signs of this theoretical emission in X-ray data collected by XMM-Newton since its launch in 1999. By analyzing the properties of the X-ray emission of interstellar iron recorded by the satellite, they found the signatures of a large fast ion population in the vicinity of the Arches cluster, about one hundred light-years from the center of the Milky Way. The stars in this cluster are traveling together at a speed of approximately 700,000 km/h. The cosmic rays are in all likelihood produced in the high-speed collision of the star cluster with a gas cloud in its path. In this particular region, the energy density of the accelerated ions is around a thousand times greater than that of cosmic rays in the neighborhood of the Solar System.

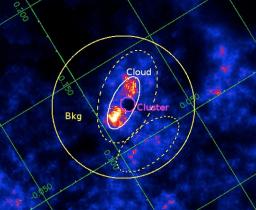
The region of the Arch cluster seen in X-rays (contours) and in near-infrared (background image). The infrared image is obtained from observations of the Hubble telescope at the 1,875 micron wavelength. The contours indicate the intensity of the neutral iron line observed by the XMM-Newton satellite around the star cluster (located in the image centre) The X-ray emission is produced by cosmic-rays accelerated in a shock produced by the rapid motion of the stars. Crédits :ESA-XMM/NASA-HST/ CNRS-IN2P3-CSNSM/CEA-SAp.
This is the first time that a major source of low-energy cosmic rays [5] has been discovered outside the Solar System. It shows that the shock waves of supernovae are not the only objects that can cause mass acceleration of atomic nuclei in the Galaxy. These findings should make it possible to identify new sources of ions in the interstellar medium, and may lead to a better understanding of the effects of these energetic particles on star formation.
Contact :
Publications :
"Nonthermal X-rays from low-energy cosmic rays: Application to the 6.4 keV line emission from the Arches cluster region"
V. Tatischeff, A. Decourchelle, and G. Maurin, dans Astronomy & Astrophysics, vol 546, A88 (octobre 2012),
(for an electronic version  fichier PDF)
fichier PDF)
see - the CEA press release (11 ocobre 2012)
- the CNRS press release (11 octobre 2012)
Notes :
[1] XMM-Newton is a satellite built by ESA with major contributions from the CNES, CEA and CNRS.
[2] Laboratories involved : Centre de Spectrométrie Nucléaire et de Spectrométrie de Masse (CNRS/Université Paris-Sud 11), Laboratoire d'Annecy le Vieux de Physique des Particules (CNRS/Université de Savoie), Laboratoire Astrophysique, Interactions, Multi-échelles (CEA/CNRS/Université Paris-Diderot).
[3] CEA Institut de recherches sur les lois fondamentales de l'Univers (Irfu), Astrophysical Department.
[4] Those with kinetic energie lower than 0,5 billion électronvolts.
[5] The cosmic-rays discovered are hadronic, meaning that they are in great majority atom nuclei. The hadronic cosmic-rays constitute 99% of the galactic particles detected at the Earth. The electrons and positrons (the leptonic component) are much less numerous.
• Structure and evolution of celestial bodies
• Department of Astrophysics (DAp) // UMR AIM