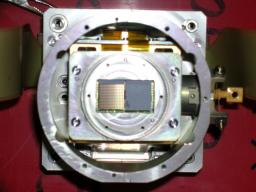
A prototype (called P-Artemis) has been tested at APEX in March 2007 at 450 microns (one small array of 256 bolometers). The goal was to demonstrate the feasibility and scientific potential of the full instrument. The P-Artemis array used for these tests is a 16x16-pixel PACS-like detector array that was not selected for Herschel and was modified to operate at 450 microns by adding a silicon layer on its surface (anti-reflecting layer). Another test will be made in November 2007, with an improved version of the prototype (a factor ~3 in performances is expected).
This table sums up the expected (Artemis) and measured (P-Artemis) performances of the instrument.
| Instrument |
Wavelength |
FOV |
Beam |
Pixel |
NEFDa |
Relative |
| ArTéMiS/APEX |
200 |
1.8'x1.8' |
4.2'' |
1.7'' |
410 |
4 |
| P-ArTéMiS/APEX |
200 |
0.5'x0.5' |
4.2'' |
1.7'' |
1500 |
0.01 |
| SHARC-2 | 350 | 0.9'x2.5' | 8.5'' | 4.8'' | 1000 | 1 |
| SCUBA-2 | 450 | 8'x8' | 7.5'' | 6.2'' | 600 | 40 |
(a) : For the Artemis case, this is the expected NEFD assuming an elevation of 50 degrees, a PWV=0.6 mm at 350 and 450 microns and PWV=0.2 mm at 200 microns.
(b) : Imaging Speed relative to SHARC-2 on the CSO at 350 microns for mapping cold dust emission. This is defined as the speed with which areas of the sky can be imaged to a given equivalent surface brightness sensitivity. The wavelength normalization assumes a dust temperature of 15K and a dust emissivity index of 1.5.
(c) : Numbers in parentheses represent the best theoretical performances. The P-Artemis detectors are not fully optimized for ground-based conditions as they are "free" arrays not selected for Herschel.
(*) Artemis stands for "Architectures de bolometres pour des Telescopes a grand champ de vue dans le domaine sub-Millimetrique au Sol" in French.
• ArTéMiS