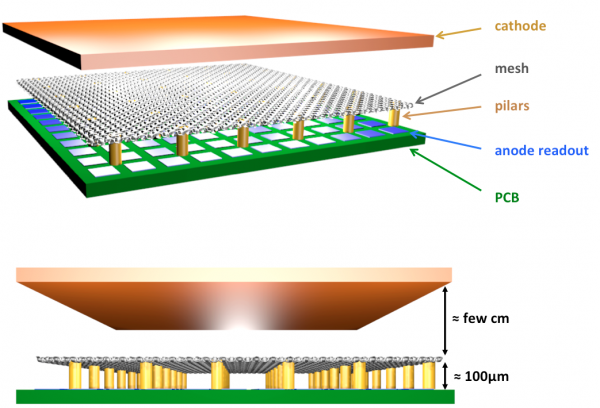
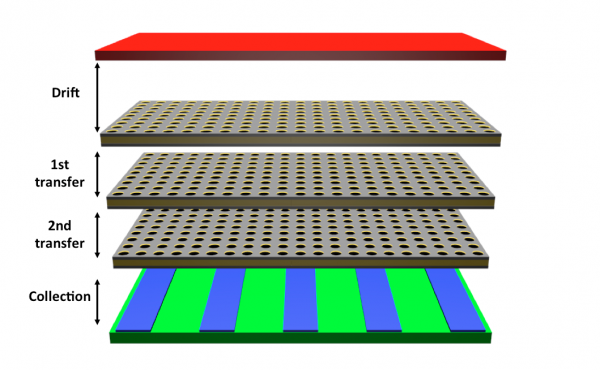
Micromegas (MICRO-MEsh-GAseous Structure) is a two-stage avalanche chamber with a narrow amplification gap defined by the anode plane and a thin micromesh, and a drift region with dimensions that range between a few mm and a few meters depending on the application. The parallelism between the micromesh and the anode is maintained by insulator spacers that are normally layed down by means of conventional lithography.
Due to the large asymmetry in the field configuration, (Eamp >> Edrift ) that produces a funnel shape of the electric field around the holes, when a charged particle enters the drift region, the primary electrons produced by ionisation drift towards the amplification gap thanks to the constant electric field, Edrift. In the amplification gap an avalanche process takes place due to the large amplification electric feld, Eamp.
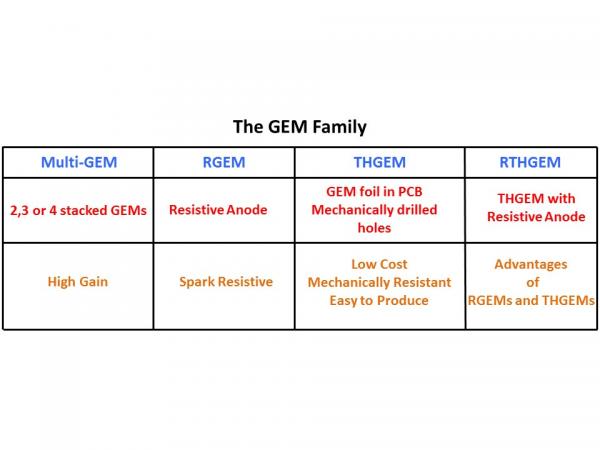
The GEM consists of a thin copper clad film, i.e. copper, insulator, copper and the insulator being often 50 µm kapton that has been chemically etched to obtain a high density of holes. When applying a potential difference between the two sides of the GEM, the electric field generated concentrates the field lines through the holes to work as amplification regions. When placing a drift electrode above the GEM foil, the electrons released by the primary ionisation drift into the holes where amplification takes place in the high electric field. The avalanche electrons will be transferred into the gap below the GEM. Normally several (2, 3 or 4) GEMs are used together in order to distribute the gas gain over several gaps reducing the risk of discharges. The hole diameter is typically of the order of 25-150 µm with a distance between holes of 50-200 µm.