|
DUNE |
 |
|---|
A space telescope for the study of the Dark Universe
The purpose of the DUNE mission (acronym for "Dark UNiverse Explorer") is to shed light on the "dark" components of the Universe with a wide field imager in space.
The recent measurements of the Cosmic Microwave Background anisotropies, Supernovae Ia, and large-scale structure concur to confirm the (lambda- CDM) cosmological model. Paradoxically, this "concordance model" relies on three ingredients whose origin and nature are unknown: dark matter (CDM), dark energy (lambda) and the fundamental field(s) driving inflation. The understanding of these ingredients is likely to revolutionise fundamental physics.
To study the dark Univers, DUNE will make use of the weak gravitational lensing effect which provides a direct measure of the distribution of dark matter in the Universe. This is done by measuring the weak distortions induced by intervening large-scale structures on the images of distant galaxies. This can be used to measure cosmological parameters, and, in particularl, the dark energy equation-of-state parameter which affects the growth of cosmic structures. The wide-field imager of DUNE will circumvent atmospheric effects, which limit ground based surveys, and provide both high statistics (i.e. more resolved galaxies) and low systematics (thanks to a small and stable PSF) for weak lensing.
Another method to probe dark energy is provided by Supernovae Ia, a homogeneous class of objects which have been shown to provide excellent distance indicators. The study of dark energy with this technique requires additional filters and is a desired option for DUNE.
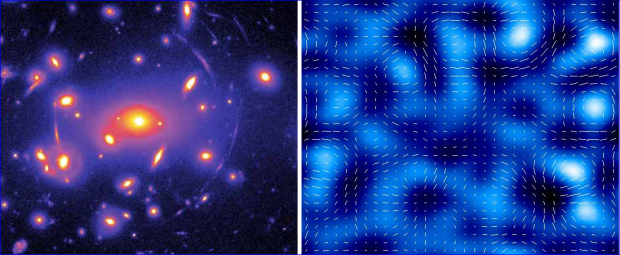
Left: Picture of the cluster of galaxies "Abell 2218" showing the distortions (arcs) of the background distant galaxies images by the intervening dark matter of the cluster (NASA/ESA-HST).
Right: Exemple of reconstitution of the dark matter distribution from the study of gravitational distortions (Reserved rights).
 See also the following link : http://www.dune-mission.net/
See also the following link : http://www.dune-mission.net/