Measurements are made with a pulsed neutron source using the time-of-flight method to determine the neutron energy. Neutrons are produced by a particle beam on a heavy material target.
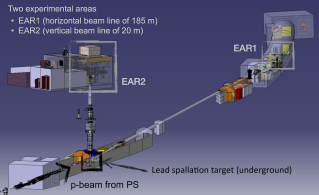
- n_TOF at Cern (20 GeV/c protons on a lead target).
- GELINA at JRC-Geel (100 MeV electrons on an uranium target).
The detection of reaction products (neutrons, gammas, fission fragments) is done by specific detectors optimized to operate in presence of neutrons.
These time-of-flight facilities are complementary. The resolution of GELINA is excellent while the instantaneous flux at CERN is extremely intense, which is an advantage for measurements with radioactive isotopes. A second beam line (20 m) is operational since 2014 at CERN.
Technical description
The pulsed source of particles produces neutrons of various energies at a given time. At a distance of typically 10 to 200 m the neutron beam interacts with the sample under study. The reaction product is detected by a suitable detector and the detection time determines the neutron flight time and therefore its incident energy.
Les détecteurs typiquement utillisés sont
- Gamma-ray detectors based on C6D6. They are used for measurements of capture cross sections (at CERN and GELINA). This type of detectors is the least sensitive to scattered neutrons.
- A 4pi detector with an efficiency close to 100%, based on 40 BaF2 crystals, is used at CERN for neutron capture measurements.
- Li-glass detectors are used at GELINA for total cross-section measurements by transmission.
- A Micromegas detector was developed for n_TOF at CERN to monitor the neutron beam profile.
- Neutron flux detectors based on 10B and 235U are used at GELINA.