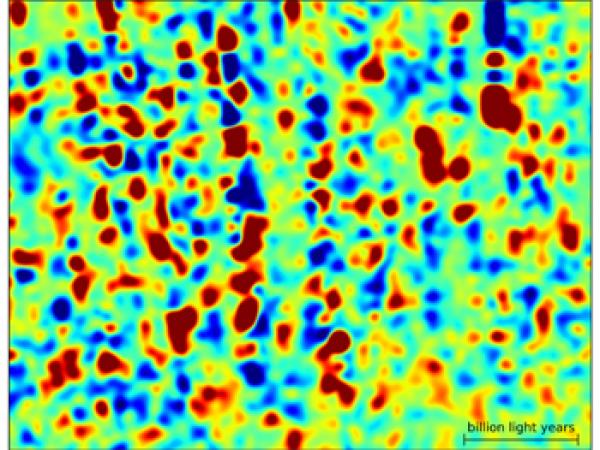
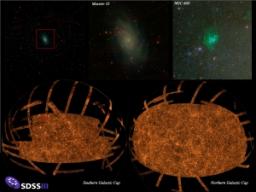
To retrace the history of the Universe, physicists need to make images of it at its different ages, going back tens of billions of years.
Scientists from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS-III), including a group from Irfu and CNRS (IN2P3 and INSU), have produced the largest map of the distant Universe from the BOSS (Baryon Oscillations Spectroscopic Survey) survey. This three-dimensional map shows the position in space and time of intergalactic hydrogen gas clouds. It was obtained using light from the brightest objects in the cosmos, quasars, which illuminate these clouds that can then be imaged. More than 14,000 quasars were used to make this first hydrogen map of the Universe, whose 3rd dimension allows us to go back in time. At the end of 2014, a new map will be established using a number of quasars ten times higher. It will then offer a new view of the Universe as it existed 11 billion years ago and will make it possible to study how the expansion of the Universe has evolved throughout its history.
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey III, a collaboration with contributions from researchers at the CNRS and CEA, has just released the widest sky survey ever carried out to the international scientific community at the annual meeting of the American Astronomy Society held in Seattle between January 10 and 13, 2011. This survey provides an image and a catalog of sources covering almost all of the sky in five colors and with a quality never before achieved in terms of the sky coverage and the accuracy of the luminosity measurements. The catalog, containing around 470 million objects (galaxies, stars, quasars, etc.), will be published in the Astrophysical Journal Supplements.
IRFU's Double Chooz group has just published some surprising results regarding the flux of antineutrinos generated by uranium and plutonium fission products in nuclear power reactors. A more precise estimate of this flux has revealed a +3% shift with respect to the predictions considered as the benchmark for the past 25 years. The re-analysis of the most important past reactor neutrino experimental results, in the light of this new flux prediction, lead to the so called 'reactor antineutrino anomaly'. Including other effects such as the evolution of the neutron lifetime and the presence of long-lived fission isotopes, the averaged shortfall in the number of antineutrinos detected at short baseline reactor experiments is almost 6%. The hypothesis according to which this anomaly can be explained by the existence of a new particle, a 4th "sterile” neutrino, ties in surprisingly well with other independent results.
If its existence is proven by forthcoming experiments this 4th neutrino, interacting only with gravity, should be added to the bestiary of the Standard Model of particle physics. It could have some impact on cosmology as well. Nonetheless, neutrino flux measurements will have to be performed less than ten meters from reactor cores to obtain irrefutable proof that the new particle exists. This is within the grasp of present-day techniques used in neutrino detection experiments, particularly in the case of Nucifer, a detector that is about to be used in a data-gathering mission on Osiris, the research reactor in Saclay. Other new proposals are being discussed by the particle physics community to test this anomaly, with new neutrino beam experiment (at CERN) or by deploying a Mci neutrino generator in large liquid scintillator detectors (like Borexino).
An international team, including scientists from the Astrophysics Department-AIM and the Particle Physics Department of CEA-Irfu, has just used the Planck satellite to discover galaxy clusters with characteristics that were previously unknown. These clusters, which contain up to a thousand galaxies, are the largest structures in the Universe. Many of them are located very far away from us, and we still know relatively little about them. Astrophysicists were able to detect the new clusters thanks to the imprint left in the background radiation of the universe by the hot gas from the clusters. Of the 189 clusters detected by Planck at distances from 1 to 5 billion light-years, 20 were previously unknown. Thanks to a joint program with the XMMNewton x-ray satellite, some of these new clusters could be observed, revealing weaker luminosity and a highly perturbed gas distribution. These must therefore be clusters with different characteristics.
These results were presented at a scientific colloquium on results from the Planck satellite, held from 10th to 14th January 2011 in Paris. They were published in a special issue of Astronomy & Astrophysics.
For a more detailed account, see also the French version.
The scientific community had to wait 18 months for the data collected by Planck, the European Space Agency satellite. Now, the first scientific results are in. The first edition of the compact sources catalog (ERCSC, Early Release Compact Sources Catalogue), with several thousand sources detected by Planck, has been published and presented in the context of an international colloquium, held from 11th to 14th January 2011 at the Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie in La Villette (Paris).
Read the joint press release from CNES, CNRS, CEA, and ESA
Also refer to the program of the colloquium
|
Contact:
|