Development and integration platform for nuclear and particle physics
For subatomic physics experiments, laboratories rely on platforms that allow them to develop R&D on detectors and microelectronics, but also to integrate them, test them and measure their performance. R&D focuses, for example, on improving the characteristics of Micromégas detectors: high flux resistance, picosecond time measurement, radiation resistance, neutron detection, high energy resolution. To meet these needs, the "MICROMEGAS FABLAB" has been developed.
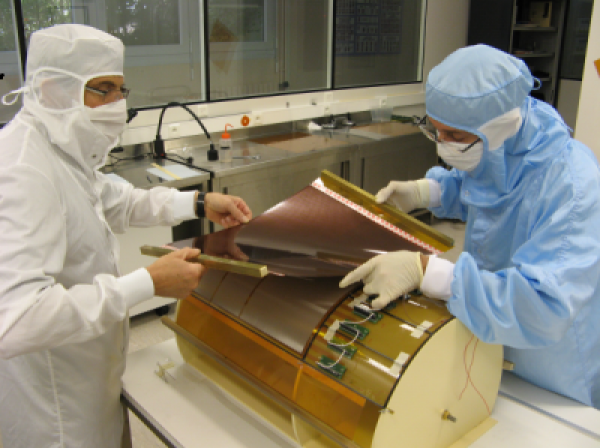

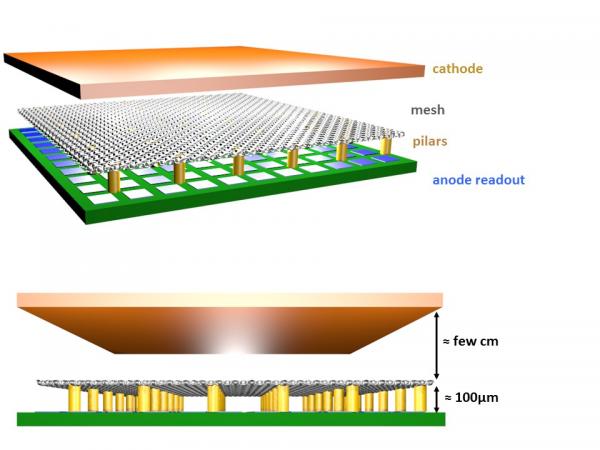
Welcome to MPGD Irfu Activities Micro-Pattern Gas Detector (MPGD) have been developed in CEA-Saclay since 1996. MPGDs are gaseous particle detectors coming from the development of wire chambers invented by Georges Charpark (Nobel prize in Physics in 1992). MPGDs can detect particles (photons, neutrons, charged particles) by amplifying the charges that have been created by ionisation in the gas volume.
Detectors for both infinite physics
In the fields of instrumentation, Irfu's teams carry out the necessary instruments to see through its research in subatomic physics, astrophysics and cosmology. From the mechanical design of detectors to the realization and characterization of prototypes, and finally the integration and testing of final detectors, there are numerous expertises such as microstructured gas detectors, imagers and space spectro-imagers in different wavelengths (gammas, X, visible, infrared and submillimetre waves).

Signal processing and real time systems
Electronic data acquisition systems are used to collect, digitize, format and process data from the detection systems that form the core of experimental physics projects. Irfu laboratories maintain and develop all the hardware, firmware and software skills required to design and implement the entire physical data detection and processing chain.
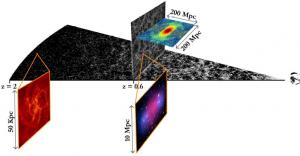
The most intriguing development in modern cosmology is to realise that the better part of the Universe is essentially of unknown nature. This conclusion relies on two types of observations. The first one is the indirect evidence since decades of the presence of a large quantity of invisible matter, called dark matter, whose gravitational influence spans all cosmic scales, from galaxy to clusters of galaxies, and the whole Universe.