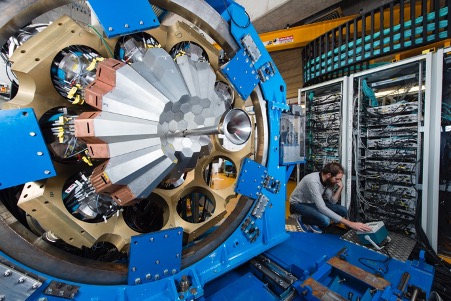
AGATA (Advanced Gamma-ray Tracking Array) is a new generation high-resolution γ-ray spectrometer providing unprecedented Doppler-correction capabilities thanks to a combination of fine detector segmentation, efficient pulse-shape analysis algorithms, and implementation of an innovative γ-ray tracking concept.
Working principle
Gamma-ray detection using semiconductor materials, such as high-purity germanium typically used for high-resolution γ-ray spectroscopy, is possible thanks to three mechanisms in which γ rays interact with matter, namely photoelectric effect, pair creation and Compton scattering. In the two former processes the total energy of a γ ray is transferred to an electron, or to an electron-positron pair, which subsequently generate a cloud of electron-hole pairs along their path in the detector material. These pairs are collected at the detector electrodes and form a signal, which amplitude is proportional to the γ-ray energy. In contrast, when the Compton scattering occurs, an electron gains only a part of the γ-ray energy, and a new photon is emitted that carries its remainder. Through a series of subsequent Compton-scattering events concluded by a photoelectric absorption the entire energy of the γ ray can be deposited in the detector. However, it is possible that a Compton-scattered photon escapes from the detector volume, and thus the registered energy will be lower than the γ-ray energy. To prevent this, so-called anti-Compton shields are typically used in high-resolution γ-ray spectroscopy, which surround the germanium detector, but are protected from a direct irradiation by thick metal collimators. Thus, if any signal is registered by the shield, it must originate from Compton scattering inside the detector, which implies that the coincident signal in the detector should be rejected. Such configuration, presented in figure (a) on the right, obviously limits the solid angle W which can be covered by germanium detectors, and, consequently, the total detection efficiency ε.
AGATA relies on a different concept, schematically presented in figure (b) on the right. The anti-Compton shields with related collimators are eliminated, and instead the entire solid angle covered by the spectrometer is filled by high-purity germanium detectors. Thanks to their fine segmentation (each germanium crystal is electrically segmented into 6 radial sectors and 6 longitudinal slices, i.e. 36 individual signals are read out) and application of pulse-shape algorithms (PSA), the 3D position of each γ-ray interaction point can be determined with a precision of ~5mm. Using the list of interaction points for each event and the corresponding deposited energies, resulting from the PSA procedure, the trajectory of the γ ray through the entire spectrometer can be reconstructed with help of sophisticated tracking algorithms. This includes possible scattering from one crystal to another, and thus events that would have been rejected by anti-Compton shields in a standard γ-ray spectrometer are recovered here, greatly increasing the detection efficiency. This innovative solution, made possible through advances in germanium detector technology, digital electronics, and pulse-shape analysis, provides also a much more precise determination of the direction of the γ-ray emission than what is achievable with conventional set-ups, which is particularly important for experiments using fast ion beams of hundreds MeV per nucleon.
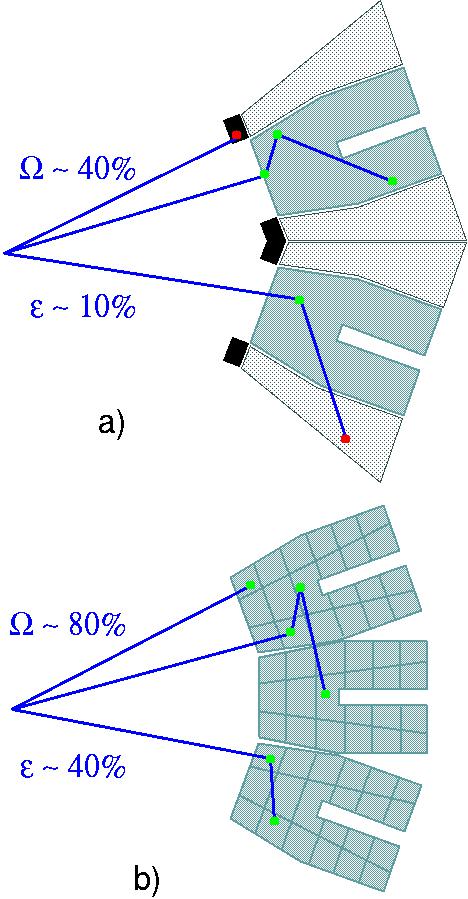
Schematic presentation of two types of gamma-ray spectrometers: (a) standard configuration with anti-Compton shields (gray) and collimators (black), (b) AGATA. Gamma-ray interaction points that contribute to the energy measured by the spectrometer are marked in green, those that are “missed” by the detectors are in red. Maximum solid angle coverage omega and efficiency epsilon for each configuration are indicated.
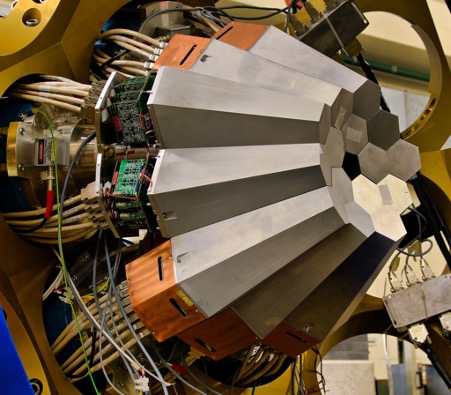
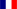
The AGATA demonstrator consisted of five triple clusters (3 asymmetric Ge detectors in a common cryostat). The surface of each diode is electrically segmented into 36 segments (i.e. 5*3*36= 540 segments for the whole and 540+15=555 measurement channels).
Timeline
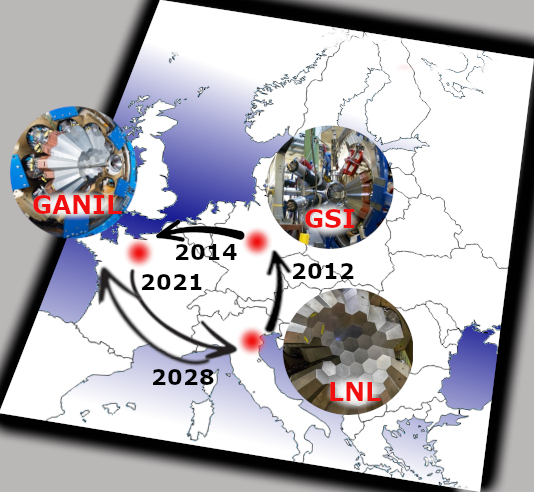
The AGATA collaboration was established in 2003, with the aim to demonstrate the feasibility of γ-ray tracking. Following successful R&D studies, a decision to construct the European 4π γ-ray tracking spectrometer has been taken. The first experiments with the so-called AGATA Demonstrator, consisting initially of 3 triple clusters (9 individual HPGe detectors), and later expanded to 5 triple clusters, were performed at Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro, Italy, starting from April 2010.
After a fruitful campaign in Legnaro, in 2012 AGATA moved to GSI, Darmstadt, Germany, where it remained for two years, and demonstrated its outstanding potential in studies using high-energy fragmentation beams. A longer campaign in GANIL, Caen, France followed, which took place from 2015 till 2021, and has seen AGATA gradually expanding to an almost 1π solid angle configuration. After major upgrades of the detector infrastructure, the array returned to LNL, where it will remain until 2028, when a move to GANIL is planned. Beyond 2030, three more European nuclear physics laboratories have expressed their willingness to host AGATA: FAIR (Darmstadt, Germany), JYFL (Jyvaskyla, Finland) and ISOLDE at CERN (Switzerland). The possible physics cases, making use of specific strengths of each facility, are outlined in the AGATA White Book (W. Korten et al, Eur. Phys. J. A 56, 137 (2020)).
The collaboration currently involves scientists from 40 institutions in 13 European countries. The Memorandum of Understanding signed by these institutions in 2021 foresees expanding AGATA to a 3π solid angle configuration (135 individual Ge detectors, or equivalently 45 triple clusters) by 2030.
Contributions from IRFU (scientific and technical)
IRFU strongly contributes to the construction, operation and exploitation of the AGATA array.
Since 2010 IRFU/DPhN scientists have been involved in many AGATA experiments, with a major contribution to:
- Lifetime measurements in neutron-rich Zn isotopes (PhD thesis of C. Louchart at DPhN; C. Louchart et al, Phys. Rev. C 87, 054302 (2013))
- The first Coulomb-excitation study of the properties of a super-deformed band (K. Hadynska-Klek et al, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 062501 (2016))
- Lifetime measurements in neutron-rich fission fragments around 100Zr, shedding light on the quantum phase transition at neutron number N=60 (PhD thesis of S. Ansari at DPhN, G. Pasqualato et al, Eur. Phys. J. A 59, 276 (2023))
- Unsafe Coulomb excitation of 106Cd (PhD thesis of D. Kalaydjieva at DPhN)
- Coulomb-excitation studies of shape coexistence in 110Cd, 96Zr and 74Se (PhD thesis of R. Kjus at DPhN, ongoing)
They also play an important role in the management of the project, as members of the AGATA Steering Committee, leaders of working groups and campaign spokespersons.
The upgrade of AGATA beyond the 1π solid angle configuration used at GANIL required a redesign of the existing low-voltage power supplies (LVPS), a new high-voltage (HV) system and a new LN2 filling system, which should satisfy the space constraints of the growing array. DIS played a key role in the design, manufacturing and maintenance of the LVPS and LN2 filling systems used in the LNL, GSI and GANIL campaigns and was responsible for the development of their upgraded versions to be used in the current campaign at LNL and beyond. In the framework of the ANR OASIS project (Optimisation of AGATA for Science) physicists from DPhN worked on the performance of AGATA pulse-shape analysis algorithms (M. Siciliano et al, Eur. Phys. J A 57, 64 (2021))
DEDIP runs one of four dedicated detector laboratories in the collaboration. While it is currently concentrating on single capsule tests, its long-term ambition is to integrate, maintain and test triple clusters.
AGATA official website: https://www.agata.org
Contacts
DPhN: M. Zielinska
DEDIP: M. Karolak
DIS: T. Joannem, A. Lotodé